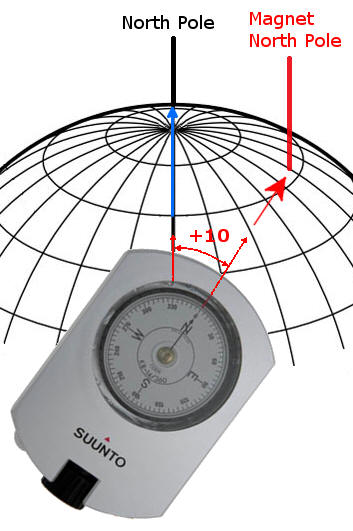
Classes
- Polyhedron
Members
(static, constant) limit :Object.<{tet:Number, oct:Number, dod:Number, ico: Number}>
Maximum subdivision level without overflowing any buffer (16 bits - 65536).
Type:
-
Object.<{tet:Number, oct:Number, dod:Number, ico: Number}>
- Source:
(static, constant) nsegments :Number
Default number of segments (points - 1) for drawing a meridian or parallel.
Type:
- Source:
(inner, constant) initialDod :Array.<vec3>
Twenty points of a dodecahedron
inscribed in the unit sphere.
Golden Ratio:
- Φ = (√5+1)/2 = 1.618033988749895
2/Φ = √5 - 1 = 1.2360679774997898
Radius of circunscribed sphere:
Edge length:
- a = 4R / ((√5 + 1)√3) = 2/Φ R/√3 = R (√5 - 1) / √3 = 0.71364417954618
Vertex coordinates:
- 1/√3 = 0.5773502691896258
- 1 / Φ√3 = (√5-1) / (2√3) = 0.35682208977309
- Φ / √3 = (√5+1) / (2√3) = 0.9341723589627158
The eight vertices of a cube:
The coordinates of the 12 additional vertices:
- (0, ±(Φ / √3), ±(1 / Φ√3))
- (±(1 / Φ√3), 0, ±(Φ / √3))
- (±(Φ / √3), ±(1 / Φ√3), 0)
Type:
- Source:
- See:
-
(inner, constant) initialIco :Array.<vec3>
Twelve points of an icosahedron
inscribed in the unit sphere.
Golden Ratio:
- Φ = (√5+1)/2 = 1.618033988749895
Radius of circunsphere:
- R = √(Φ² + 1)/2 a = 1
- r = √(Φ² + 1) = 1.902113032590307 (a=2)
Edge length:
- a = 2R / √(Φ² + 1) = 0.7639320225002103
Vertex Coordinates:
- Φ / √(Φ² + 1)) = 0.85065080835204
- 1 / √(Φ² + 1) = 0.5257311121191336
Twelve vertices:
- (0, ±1/r, ±Φ/r)
- (±1/r, ±Φ/r, 0)
- (±Φ/r, 0, ±1/r)
Type:
- Source:
- See:
-
(inner, constant) initialOcta :Array.<vec3>
Six points of an octahedron
inscribed in the unit sphere.
Radius of circunsphere:
Edge length:
- a = 2R / √2 = 1.414213562373095
Six vertices:
- (±1, 0, 0)
- (0, ±1, 0)
- (0, 0, ±1)
Type:
- Source:
- See:
-
(inner, constant) initialTet :Array.<vec3>
Four points of a tetrahedron
inscribed in the unit sphere, in three different vertex arrangements.
Radius of circunsphere:
Radius of circuncircle:
- r = a/√3 = 2/3 √6 / √3 = 2/3 √2 = √(8/9) = 0.9428090415820634
Edge length:
- a = 4R / √6 = 2/3 √6 = 1.6329931618554523
Vertex coordinates:
- x = r sin(π/6) = √(2/9) = 0.4714045207910317
- y = r cos(π/6) = √(2/3) = 0.816496580927726
- z = 1/3 = 0.3333333333333333 (24/9 = 8/9 + (z+1)²)
Four vertices, lower face parallel to the xy plane:
- (r, 0, -z)
- (-x, y, -z)
- (-x, -y, -z)
- (0, 0, 1)
Alternatively, higher face parallel to the xy plane:
- (0, r, z)
- (y, -x, z)
- (-y, -x, z)
- (0, 0, -1)
Embedded inside a cube:
- (1/√3, 1/√3, 1/√3)
- (-1/√3, -1/√3, 1/√3)
- (-1/√3, 1/√3, -1/√3)
- (1/√3, -1/√3, -1/√3)
Type:
- Source:
- See:
-
(inner) vec3 :glMatrix.vec3
Type:
- Source:
Methods
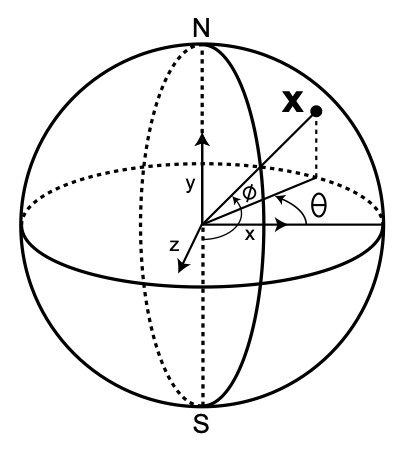
(static) cartesian2Spherical(p) → {Object.<s:Number, t:Number>}
Return a pair of spherical coordinates, in the range [0,1],
corresponding to a point p onto the unit sphere.
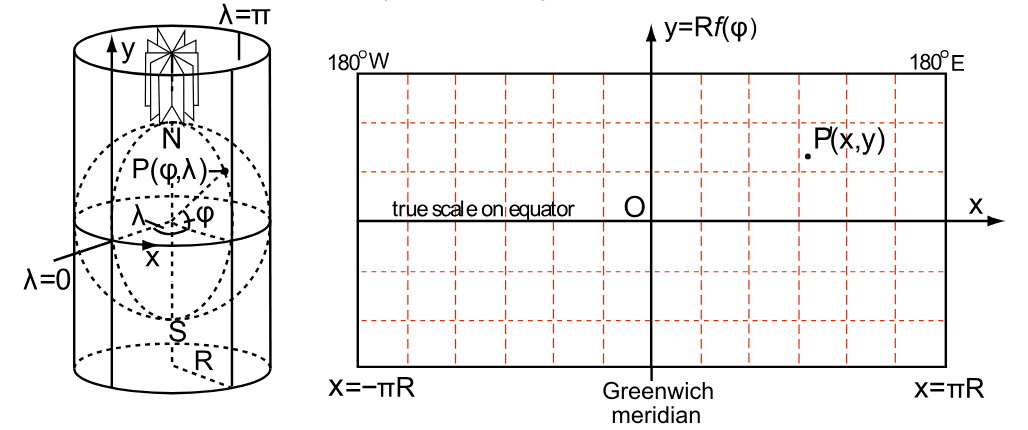
The forward projection transforms spherical coordinates into planar coordinates:
- if point p is plotted on a plane, we have the
plate carrée projection,
a special case of the equirectangular projection.
- this projection maps x to be the value of the longitude and
y to be the value of the latitude.
The singularity of the mapping (parameterization) is at φ = 0 (y = -r) and φ = π (y = r):
- In this case, an entire line at the top (or bottom) boundary of the texture is mapped onto a single point.
- In geographic coordinate system,
φ is measured from the positive y axis (North), not the z axis, as it is usual in math books.
- Therefore, we will use North-Counterclockwise Convention.
- The 'clockwise from north' convention is used in navigation and mapping.
- ________________________________________________
- atan2(y, x) (East-Counterclockwise Convention)
- atan2(x, y) (North-Clockwise Convention)
- atan2(-x,-y) (South-Clockwise Convention)
- ________________________________________________
- cos(φ-90) = sin(φ)
- sin(φ-90) = -cos(φ)
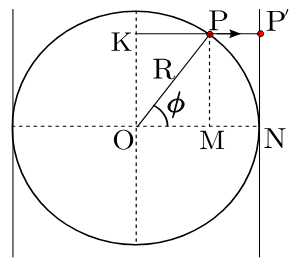
- x = r cos(θ) sin(φ)
- y = −r cos (φ)
- z = -r sin(θ) sin(φ)
- z/x = −(r sin(θ) sin(φ)) / (r cos(θ) sin(φ)) = -sin(θ) / cos(θ) = −tanθ
- θ = atan(−z/x)
- φ = acos(−y/r)
Note that this definition provides a logical extension of the usual polar coordinates notation,
with θ remaining the angle in the zx-plane and φ becoming the angle out of that plane.
Parameters:
| Name |
Type |
Description |
p |
vec3
|
a point on the sphere. |
- Source:
- See:
-
Returns:
point p in spherical coordinates:
- const [x, y, z] = p
- r = 1 = √(x² + y² + z²)
- s = θ = atan2(-z, x) / 2π + 0.5
- t = φ = acos(-y/r) / π
- tg(-θ) = -tg(θ) = tan (z/x)
- arctan(-θ) = -arctan(θ) = atan2(z, x)
Since the positive angular direction is CCW,
we can not use North-Clockwise Convention,
because the image would be rendered mirrored.
- border ≡ antimeridian
- atan2(-z, x) (border at -x axis of the image - wrap left to right) (correct form) or
- atan2(z, -x) (border at x axis of the image - wrap right to left).
- atan2(z, x) (border at x axis of the image - mirrored).
-
Type
-
Object.<s:Number, t:Number>
(static) clamp(x, min, max) → {Number}
Constrain a value to lie between two further values.
Parameters:
| Name |
Type |
Description |
x |
Number
|
value. |
min |
Number
|
minimum value. |
max |
Number
|
maximum value. |
- Source:
Returns:
min ≤ x ≤ max.
-
Type
-
Number
(static) mercator2Spherical(x, y) → {Object.<x:Number, y:Number>}
Parameters:
| Name |
Type |
Description |
x |
Number
|
longitude in [0,1]. |
y |
Number
|
latitude in [0,1]. |
- Source:
- See:
-
Returns:
spherical coordinates in [0,1].
-
Type
-
Object.<x:Number, y:Number>
(static) pointsOnAntiMeridian(nopt) → {Float32Array}
Return an array with n points on the anti meridian.
Parameters:
| Name |
Type |
Attributes |
Default |
Description |
n |
Number
|
<optional>
|
nsegments
|
number of points. |
- Source:
Returns:
points on the anti meridian.
-
Type
-
Float32Array
(static) pointsOnEquator(nopt) → {Float32Array}
Return an array with n points on the equator.
Parameters:
| Name |
Type |
Attributes |
Default |
Description |
n |
Number
|
<optional>
|
nsegments
|
number of points. |
- Source:
Returns:
points on the equator.
-
Type
-
Float32Array
(static) pointsOnMeridian(longitudeopt, nopt, antiopt) → {Float32Array}
Return an array with n points on a meridian given its
longitude.
Parameters:
| Name |
Type |
Attributes |
Default |
Description |
longitude |
Number
|
<optional>
|
0
|
distance east or west of the prime meridian: [-180°,180°] |
n |
Number
|
<optional>
|
nsegments
|
number of points. |
anti |
Boolean
|
<optional>
|
false
|
whether to draw the antimeridian also. |
- Source:
Returns:
points on the meridian.
-
Type
-
Float32Array
(static) pointsOnParallel(latitudeopt, nopt) → {Float32Array}
Return an array with n points on a parallel given its
latitude.
Parameters:
| Name |
Type |
Attributes |
Default |
Description |
latitude |
Number
|
<optional>
|
0
|
distance north or south of the Equator: [-90°,90°]. |
n |
Number
|
<optional>
|
nsegments
|
number of points. |
- Source:
Returns:
points on the parallel.
-
Type
-
Float32Array
(static) pointsOnPrimeMeridian(nopt) → {Float32Array}
Return an array with n points on the prime meridian.
Parameters:
| Name |
Type |
Attributes |
Default |
Description |
n |
Number
|
<optional>
|
nsegments
|
number of points. |
- Source:
Returns:
points on the prime meridian.
-
Type
-
Float32Array
(static) radians(deg) → {Number}
Convert degrees to radians.
Parameters:
| Name |
Type |
Description |
deg |
Number
|
angle in degrees. |
- Source:
Returns:
angle in radians.
-
Type
-
Number
(static) rotateUTexture(obj, degrees)
Rotate u texture coordinate by a given angle.
Parameters:
- Source:
(static) setMercatorCoordinates(obj)
Set Mercator vertex coordinates.
Parameters:
- Source:
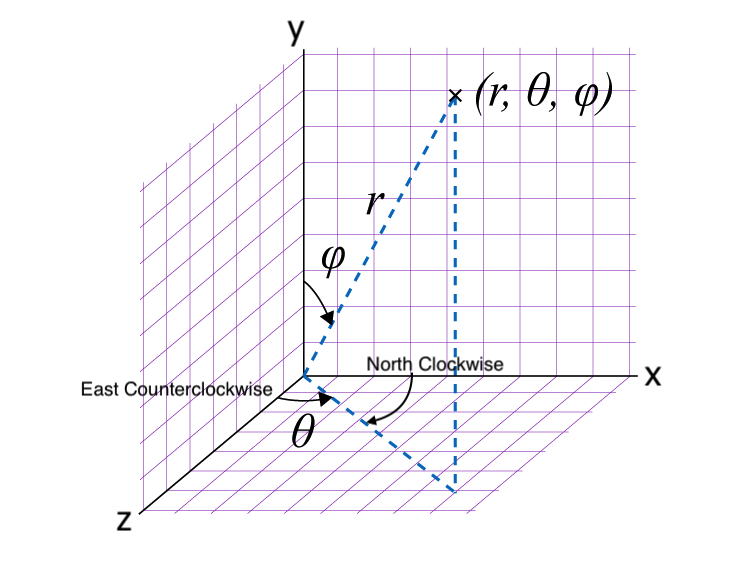
(static) spherical2Cartesian(s, t, r) → {vec3}
Return a point on the unit sphere given their
spherical coordinates: (θ, φ, r=1).
It is assumed that:
- the two systems have the same origin,
- the spherical reference plane is the Cartesian xz plane,
- φ is inclination from the y direction, and
- the azimuth is measured from the Cartesian x axis, so that the x axis has θ = 0° (prime meridian).
- x = p[0] = r cos(θ) * sin(φ)
- z = p[2] = -r sin(θ) * sin(φ)
- y = p[1] = -r cos(φ)
Parameters:
| Name |
Type |
Description |
s |
Number
|
azimuth angle θ, 0 ≤ θ ≤ 2π. |
t |
Number
|
zenith angle φ, 0 ≤ φ ≤ π. |
r |
Number
|
radius distance, r ≥ 0. |
- Source:
- See:
-
Returns:
cartesian point onto the unit sphere.
-
Type
-
vec3
(static) spherical2Mercator(s, t) → {Object.<x:Number, y:Number>}
Convert a 2D point in spherical coordinates to a 2D point in
Mercator coordinates.
The Mercator projection is a map projection that was widely used for navigation,
since loxodromes
are straight lines (although great circles are curved).
The following
equations
place the x-axis of the projection on the equator,
and the y-axis at longitude θ
0, where θ is the longitude and φ is the latitude:
- x = θ - θ0, 0 ≤ θ - θ0 ≤ 2π
- y = ∫ φ 0sec(φ) dφ = ln [tan (π/4 + φ/2)], -π/2 ≤ φ ≤ π/2 → -π ≤ y ≤ π
The poles extent to infinity. Therefore, to create a square image,
the maximum latitude occurs at y = π, namely:
- φmax = 2 atan (eπ) - π /2 = 85.051129°
As a consequence, we clamp the latitude to [-85°,85°] to avoid any artifact.
Parameters:
| Name |
Type |
Description |
s |
Number
|
longitude (horizontal angle) θ, 0 ≤ θ ≤ 1. |
t |
Number
|
latitude (vertical angle) φ, 0 ≤ φ ≤ 1. |
- Source:
- See:
-
Returns:
mercator coordinates in [0,1].
-
Type
-
Object.<x:Number, y:Number>
Type Definitions
polyData
An object containing raw data for
vertices, normal vectors, texture coordinates, mercator coordinates and indices.
Polyhedra have no index.
Type:
Properties:
| Name |
Type |
Description |
vertexPositions |
Float32Array
|
vertex coordinates. |
vertexNormals |
Float32Array
|
vertex normals. |
vertexTextureCoords |
Float32Array
|
texture coordinates. |
vertexMercatorCoords |
Float32Array
|
mercator texture coordinates. |
indices |
Uint16Array
|
index array. |
name |
String
|
polyhedron name. |
nfaces |
Number
|
initial number of triangles. |
maxNumSubdivisions |
Number
|
maximum number of subdivisions. |
ntri |
function
|
return the number of triangles given the level of detail. |
level |
function
|
return the level of detail given the number of triangles. |
- Source: