Members
axis :String
Type:
- String
axisBuffer :WebGLBuffer
Type:
- WebGLBuffer
axisColorBuffer :WebGLBuffer
Type:
- WebGLBuffer
(constant) axisColors :Float32Array
Type:
- Float32Array
(constant) axisVertices :Float32Array
Type:
- Float32Array
colorShader :WebGLShader
Type:
- WebGLShader
(constant) eye :Array.<Number>
Type:
- Array.<Number>
gl :WebGLRenderingContext
Type:
- WebGLRenderingContext
indexBuffer :WebGLBuffer
Type:
- WebGLBuffer
(constant) lblslices :HTMLElement
Type:
- HTMLElement
(constant) lblstacks :HTMLElement
Type:
- HTMLElement
lightingShader :WebGLShader
Type:
- WebGLShader
lineBuffer :WebGLBuffer
Type:
- WebGLBuffer
lines :Float32Array
Type:
- Float32Array
modelMatrix :Matrix4
Type:
mscale :Number
Type:
- Number
normal :Float32Array
Type:
- Float32Array
normalBuffer :WebGLBuffer
Type:
- WebGLBuffer
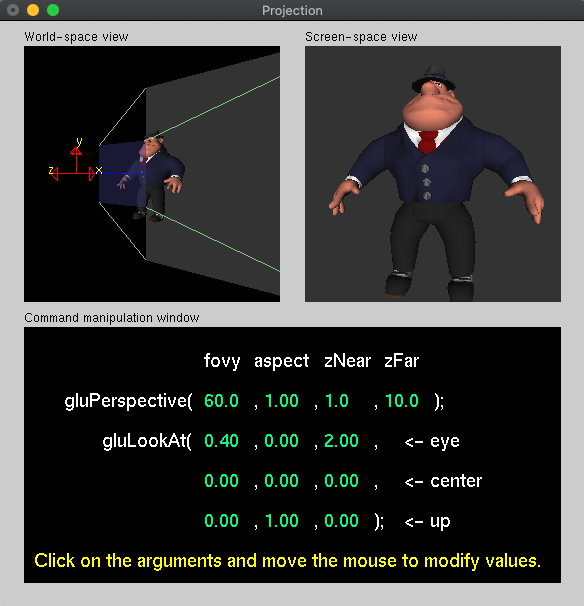
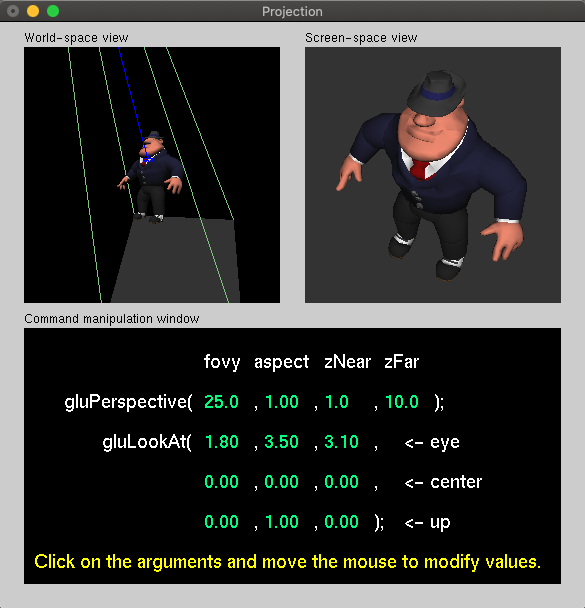
(constant) projection :Matrix4
For projection, we can either use:
- An orthographic projection, specifying
the clipping volume explicitly:
- const projection = new Matrix4().setOrtho(-1.5, 1.5, -1, 1, 4, 6);
- Or the same perspective projection, using the Frustum function with:
- a 30 degree field of view, and a near plane at 4,
which corresponds to a view plane height of: 4 * tan(15) = 1.07 - const projection = new Matrix4().setFrustum(-1.5 * 1.07, 1.5 * 1.07, -1.07, 1.07, 4, 6);
- a 30 degree field of view, and a near plane at 4,
- Or a perspective projection specified with a
field of view, an aspect ratio, and distance to near and far
clipping planes:
- const projection = new Matrix4().setPerspective(30, 1.5, 0.1, 1000);
Type:
rotator :SimpleRotator
Type:
(constant) selector :Object
Type:
- Object
Properties:
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
lines |
Boolean | mesh visible/invisible |
texture |
Boolean | model surface visible/invisible |
axes |
Boolean | axes visible/invisible |
paused |
Boolean | animation on/off |
(constant) sl :HTMLElement
Type:
- HTMLElement
slices :Number
Type:
- Number
- Source:
- See:
(constant) st :HTMLElement
Type:
- HTMLElement
stacks :Number
Type:
- Number
- Source:
- See:
(constant) teapotModel :modelData
Type:
- Source:
theModel :modelData
Type:
vertexBuffer :WebGLBuffer
Type:
- WebGLBuffer
vertexNormalBuffer :WebGLBuffer
Type:
- WebGLBuffer
(constant) viewDistance :Number
Type:
- Number
(constant) viewMatrix :Matrix4
View matrix.
One strategy is to identify a transformation to our camera frame then invert it.Therefore, the camera transformation takes (0,0,0) to the camera position.
rotate(30, 0, 1, 0) * rotate(-45, 1, 0, 0) * translate(0, 0, 5)
camera transformation:
0.8660253882408142 -0.3535533845424652 0.3535533845424652 1.7677669525146484
0 0.7071067690849304 0.7071067690849304 3.535533905029297
-0.5 -0.6123723983764648 0.6123723983764648 3.061861991882324
0 0 0 1
translate(0, 0, -5) * rotate(45, 1, 0, 0) * rotate(-30, 0, 1, 0)
view matrix:
0.8660253882408142 0 -0.5 0
-0.3535533845424652 0.7071067690849304 -0.6123723983764648 0
0.3535533845424652 0.7071067690849304 0.6123723983764648 -5
0 0 0 1
The view matrix is the inverse of the camera's transformation matrix: viewMatrix = camera ⁻¹.
- The camera's transformation matrix takes something that's local to the camera
and transforms it to world space
(transforming the point [0,0,0] will give you the camera's position) - The view matrix takes something that's in world space and transforms it
so that it's local to the camera
(transforming the camera's position will give you [0, 0, 0])
LookAt functions from math libraries are just a convenience, indeed, and requires a view point, a point to look at, and a direction "up", for camera orientation:
The approximate view point here is: [1.77, 3.54, 3.06]
const viewMatrix = new Matrix4().setLookAt( ...eye, // view point 0, 0, 0, // at - looking at the origin 0, 1, 0); // up vector - y axis or using the glmatrix package const viewMatrix = mat4.lookAt( [], // mat4 frustum matrix will be written into eye, // view point [0, 0, 0], // look at (center) [0, 1, 0]); // view up
Type:
- Source:
- See:
yNorth :Boolean
Type:
- Boolean
- Source:
Methods
animate() → {loop}
Returns:
- Type
- loop
createEvent(key) → {KeyboardEvent}
Parameters:
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
key |
String | char code. |
Returns:
- Type
- KeyboardEvent
createModel(shape, chi) → {modelData}
Sets up all buffers for the given (triangulated) model (shape).
Uses the webgl vertex buffer, normal buffer, texture buffer and index buffer, created in mainEntrance.Then, binds each one of them as an array buffer and copies the corresponding shape array data to them.
Also, the Euler characteristic for the model is:
- χ = 2 − 2g − b
The number of triangles must be even for a valid triangulation of the sphere:
- V - E + T = 2 (sphere)
- V - E + T = 0 (torus)
Parameters:
| Name | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
shape |
modelData | a BREP model given as an IFS. | |
chi |
Number | null | 2 | model Euler Characteristic. |
- Source:
- See:
Returns:
- Type
- modelData
createProgram(gl, vshader, fshader) → {WebGLProgram}
Parameters:
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
gl |
WebGLRenderingContext | GL context. |
vshader |
String | a vertex shader program. |
fshader |
String | a fragment shader program. |
Returns:
- Type
- WebGLProgram
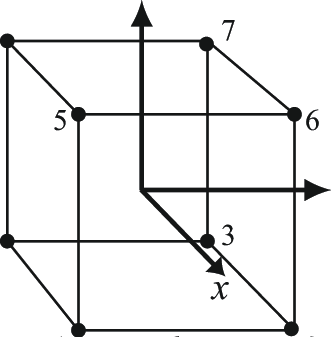
cube(side) → {modelData}
Create a model of a cube, centered at the origin.
This is not a particularly good format for a cube, since an IFS representation has a lot of redundancy.Parameters:
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
side |
Number | the length of a side of the cube. If not given, the value will be 1. |
- Source:
Returns:
- Type
- modelData
draw()
drawAxes()
Draws the axes.
Uses the colorShader.drawLines()
Draws the mesh edges and normals.
Uses the colorShader.drawModel()
Draws the model, by using the lightingShader.
If theModel.indices is defined, then calls drawElements. Otherwise, drawArrays.Since three.js version 125, THREE.Geometry was deprecated and replaced by THREE.BufferGeometry, which always define indices for efficiency.
getChar(event) → {String}
Parameters:
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
event |
KeyboardEvent | key pressed. |
Returns:
- Type
- String
getModelData(geom) → {modelData}
Polyhedra have no index.
Parameters:
- Source:
Returns:
- Type
- modelData
getModelMatrix() → {Matrix4}
Returns:
- Type
- Matrix4
getWebGLContext(canvas, opt_debug) → {WebGL2RenderingContext}
Parameters:
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
canvas |
HTMLCanvasElement | <canvas> element. |
opt_debug |
Boolean | flag to initialize the context for debugging. |
- Deprecated:
- since WebGL2
- Source:
- See:
Returns:
- Type
- WebGL2RenderingContext
handleKeyPress(event) → {key_event}
Parameters:
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
event |
KeyboardEvent | keyboard event. |
Returns:
- Type
- key_event
initShaders(GL, vshader, fshader) → {Boolean}
Parameters:
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
GL |
WebGLRenderingContext | context. |
vshader |
String | a vertex shader program. |
fshader |
String | a fragment shader program. |
- Source:
Returns:
- Type
- Boolean
loadShader(gl, type, source) → {WebGLShader}
Parameters:
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
gl |
WebGLRenderingContext | GL context. |
type |
gl.VERTEX_SHADER | gl.FRAGMENT_SHADER | the type of the shader object to be created, |
source |
DOMString | shader program. |
- Source:
- See:
Returns:
- Type
- WebGLShader
mainEntrance()
Entry point when page is loaded.
Load all data into the buffers (just once) before proceeding.- Source:
- See:
makeCube(create_indices) → {Object}
Creates a unit cube, centered at the origin, and set its properties: vertices, normal vectors, texture coordinates, indices and colors.
For a proper specular reflection on planar faces, such as a cube or a polyhedron, the normal vectors have to be perpendicular to the plane of each face.
Computing an average normal, like is done here when creating indices, is what one would want to do for a smooth object like a sphere.
The resulting rendering is very unpleasant, in this case. The right course is creating three duplicate vertices per cube corner.Even if cube.indices is not defined here, drawModel can handle it.
Parameters:
| Name | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
create_indices |
Boolean | false | whether to generated vertex indices or not. |
Properties:
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
cube.numVertices |
Number | number of vertices (36). |
cube.vertices |
Float32Array | vertex coordinate array (108 = 36 * 3). |
cube.normals |
Float32Array | vertex normal array (108 = 36 * 3). |
cube.colors |
Float32Array | vertex color array (144 = 36 * 4). |
cube.texCoords |
Float32Array | vertex texture array (72 = 36 * 2). |
cube.indices |
Uint16Array | vertex index array (36 = 6 * 2 * 3). |
Returns:
- Type
- Object
makeNormalMatrixElements(model, view) → {Float32Array}
Matrix for taking normals into eye space.
Returns a matrix to transform normals, so they stay perpendicular to surfaces after a linear transformation.Parameters:
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
model |
Matrix4 | model matrix. |
view |
Matrix4 | view matrix. |
- Source:
- See:
Returns:
- Type
- Float32Array
ring(innerRadius, outerRadius, slices) → {modelData}
Creates a model of an annulus or disk lying in the xy plane, centered at the origin.
This is not a great representation, since all the normals are the same.Parameters:
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
innerRadius |
Number | the radius of the hole in the radius; a value of
zero will give a disk rather than a ring. If ommited, the default value is 0.25. |
outerRadius |
Number | the radius of the ring, from the center to the
outer edge. Must be greater than innerRadius. If ommited, the default value is 2*innerRadius if innerRadius > 0 or 0.5 otherwise. |
slices |
Number | the number of radial subdivisions in the circular approximation of an annulus, minimum 3, default 32. |
- Source:
Returns:
- Type
- modelData
selectModel(c)
Parameters:
| Name | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
c |
Boolean | true | whether to set the sliders or not. |
setNorth(vertices, normals)
Rotate the given model so the y-axis points North.
The variable yNorth must be true, otherwise this function has no effect:- if (yNorth) (x, y, z) → (-x, z , y)
Parameters:
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
vertices |
Float32Array | vertex array. |
normals |
Float32Array | normal array. |
- Source:
setSlicesVisible(visible)
Parameters:
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
visible |
Boolean | whether to show the slices slider. |
setSliders(stk, stkmin, stkmax, slc, stkmin, slcmax)
Parameters:
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
stk |
Number | number of stacks. |
stkmin |
Number | minimum number of stacks. |
stkmax |
Number | maximum number of stacks. |
slc |
Number | number of slices. |
stkmin |
Number | minimum number of slices. |
slcmax |
Number | maximum number of slices. |
setStacksVisible(visible)
Parameters:
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
visible |
Boolean | whether to show the stacks sliders. |
uvCone(radius, height, slices, stacks, noBottom) → {modelData}
Defines a model of a cone.
The axis of the cone is the z-axis, and the center is at (0,0,0).Parameters:
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
radius |
Number | the radius of the cone |
height |
Number | the height of the cone. The cone extends from -height/2 to height/2 along the z-axis, with the tip at (0,0,height/2). |
slices |
Number | the number of slices, like the slices of an orange, minimum 3, default 32. |
stacks |
Number | the number of stacks, like horizontal cuts of an orange, minimum 1, default 16. |
noBottom |
Boolean | if missing or false, the cone has a bottom; if set to true,
the cone does not have a bottom. The bottom is a disk at the wide end of the cone. |
- Source:
- See:
Returns:
- Type
- modelData
uvCylinder(radius, height, slices, stacks, noTop, noBottom) → {modelData}
Defines a model of a cylinder.
The axis of the cylinder is the z-axis, and the center is at (0,0,0).Parameters:
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
radius |
Number | the radius of the cylinder |
height |
Number | the height of the cylinder. The cylinder extends from -height/2 to height/2 along the z-axis. |
slices |
Number | the number of slices, like the slices of an orange, minimum 3, default 32. |
stacks |
Number | the number of stacks, like horizontal cuts of an orange, minimum 1, default 16. |
noTop |
Boolean | if missing or false, the cylinder has a top; if set to true,
the cylinder does not have a top. The top is a disk at the positive end of the cylinder. |
noBottom |
Boolean | if missing or false, the cylinder has a bottom; if set to true,
the cylinder does not have a bottom. The bottom is a disk at the negative end of the cylinder. |
- Source:
- See:
Returns:
- Type
- modelData
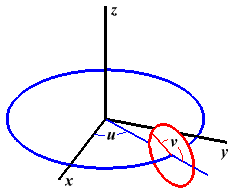
uvSphere(radius, slices, stacks) → {modelData}
Create a model of a sphere.
The z-axis is the axis of the sphere with the north pole on the positive z-axis and the center at (0,0,0).The number of triangles is 2 * slices * stacks, e.g., 48 * 24 * 2 = 2304.
However, two rows and one column of vertices have been duplicated.
Without vertex duplication,
the number of triangles would be 48 * 23 * 2 = 2208.
In fact, this is topologically a cylinder whose vertices on the two borders
have the same coordinates of the sphere north/south poles, respectively:
- uvSphere(radius, slices, stack) ≍ uvCylinder(r, height, slices, stack, true, true)
Parameters:
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
radius |
Number | the radius of the sphere, default 0.5 if not specified. |
slices |
Number | the number of lines of longitude, minimum 3, default 32 |
stacks |
Number | the number of lines of latitude plus 1, minimum 2, default 16. (This is the number of vertical slices, bounded by lines of latitude, the north pole and the south pole.) |
- Source:
- See:
Returns:
- Type
- modelData
uvSphereND(radius, slices, stacks) → {modelData}
Create a model of a sphere.
The z-axis is the axis of the sphere with the north pole on the positive z-axis and the center at (0,0,0).This version does not duplicate vertices on the seam, but it does require Tarini's method when texturing.
Parameters:
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
radius |
Number | the radius of the sphere, default 0.5 if not specified. |
slices |
Number | the number of lines of longitude, minimum 3, default 32 |
stacks |
Number | the number of lines of latitude plus 1, minimum 2, default 16. (This is the number of vertical slices, bounded by lines of latitude, the north pole and the south pole.) |
- Source:
- See:
Returns:
- Type
- modelData
uvTorus(outerRadius, innerRadius, slices, stacks) → {modelData}
Create a model of a torus (surface of a doughnut).
The z-axis goes through the doughnut hole, and the center of the torus is at (0,0,0).Parameters:
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
outerRadius |
Number | the distance from the center to the outside of the tube, 0.5 if not specified. |
innerRadius |
Number | the distance from the center to the inside of the tube, outerRadius/3 if not
specified. (This is the radius of the doughnut hole.) |
slices |
Number | the number of lines of longitude, minimum 3, default 32. These are slices parallel to the z-axis and go around the tube the short way (through the hole). |
stacks |
Number | the number of lines of latitude plus 1, minimum 2, default 16. These lines are perpendicular to the z-axis and go around the tube the long way (around the hole). |
- Source:
- See:
Returns:
- Type
- modelData
vecLen(v) → {Number}
Parameters:
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
v |
Array.<Number> | n-D vector. |
Returns:
- Type
- Number
Type Definitions
key_event(event)
Handler for keydown events.
Parameters:
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
event |
KeyboardEvent | keyboard event. |
loop()
- Source:
- See:
modelData
Polyhedra have no index.
Type:
- Object
Properties:
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
vertexPositions |
Float32Array | vertex coordinates. |
vertexNormals |
Float32Array | vertex normals. |
vertexTextureCoords |
Float32Array | texture coordinates. |
indices |
Uint16Array | Uint32Array | index array. |
- Source:
Events
clickArrowDown
clickArrowUp
clickMesh
clickRot
keydown
Key handler.
Calls handleKeyPress whenever any of these keys is pressed:- Space
- x, y, z
- p, s, T, o
- a, k, l
load
- Source:
- See:
slices
Appends an event listener for events whose type attribute value is input.
Fired when a <input type="range"> is in the Range state (by clicking or using the keyboard).
The callback argument sets the callback that will be invoked when the event is dispatched. Executed when the slices slider is changed.Parameters:
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
event |
Event | a generic event. |
stacks
Appends an event listener for events whose type attribute value is input.
Fired when a <input type="range"> is in the Range state (by clicking or using the keyboard).
The callback argument sets the callback that will be invoked when the event is dispatched. Executed when the stack slider is changed.Parameters:
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
event |
Event | a generic event. |